Job Responsibilities of a Marine Electrician. Electromechanic (ship) Job description
297. The watch electrician is directly subordinate to the watch mechanic, and in terms of special issues of the operation of electrical equipment - to the electromechanic and is the head of the watch of electricians.
The shift electrician (on electric ships) in terms of the implementation of the operating mode of the propulsion electrical installation is subordinate to the watch commander.
298. The watch electrician, when taking over the watch, is obliged:
(01) to receive from the electromechanic handing over the watch information characterizing the operation of the ship's electrical equipment, information on the observed malfunctions in its operation, on ongoing maintenance and repair work and to get acquainted with all the comments and orders transmitted by the watch;
(02) check the condition and operation of the ship's electrical equipment and read the entries in the electrical logbook.
299. The watch electrician is obliged:
(01) provide set mode work and compliance with the rules for the technical operation of electrical equipment, instructions and instructions of the electrician for its maintenance, monitor the implementation of labor safety rules and fire safety when working with him;
(02) ensure that generators are switched on and off and electricity is supplied to consumers in accordance with the orders of the engineer on duty;
(03) to report all detected malfunctions of electrical equipment to the watch mechanic and electromechanic, to take measures to eliminate them;
(04) take measures to ensure the fire safety of the ship's electrical equipment;
(05) when leaving the engine room, inform the engineer on duty about the place of his stay.
300. If there are any doubts regarding the keeping of the watch, or the need for assistance, the electrician on duty is obliged to call the electrician to the engine room.
301. The presence of an electromechanic in the engine room does not relieve the watch electrician of responsibility for keeping watch until the electrician takes control of the electrical equipment.
302. Watch electrician may turn off electrical equipment responsible appointment only with the knowledge and permission of the engineer on duty.
303. On a running watch on an electric ship, the watch electrician is obliged:
(01) strictly observe the mode of operation of the propulsion electrical installation transmitted from the navigation bridge;
(02) rehearse and execute commands from the navigation bridge. If the execution of a command (instruction) is associated with a threat of an accident or a danger to people's lives, immediately report this to the watch chief and watch mechanic; when ordered again, execute the last command (instruction), making an appropriate entry in the electrical journal and reporting the received command (instruction) to the electromechanic.
When controlling the propulsion electrical installation from the navigation bridge, the electrician on duty has the right to leave with the permission of the engineer on duty, but must be ready at any time to immediately arrive at the control station and take control of the propulsion electrical installation.
Electro Engineer111. The senior electrician reports to the chief (senior) mechanic and is the head of the electrical personnel.
It is in charge of: sources of electricity - main (main and auxiliary generators on ships with electric propulsion, generators with autonomous drive and shaft generators on ships without electric propulsion), emergency power stations from the shore, propulsion electrical installation, main and emergency switchboards, other switchgear ; electrical equipment of posts and control panels, electrical (electronic) parts of automation systems and devices, including DAU and remote control systems, all types of signaling and protection; current sewerage networks, demagnetizing devices, electric drives with ballasts and protective equipment for the mechanisms of the engine room, general ship and industrial purposes; the electrical part of the steering system (including the autopilot), machine telegraphs and axiometers, telephony, batteries with chargers and electrical measuring instruments of their department, lighting, household electrical equipment, logistics and reporting.
112. Responsibilities:
(01) to ensure the safe organization of work, reliable operation and maintenance in proper technical condition mechanisms, devices, systems, equipment, proper operation of electrical equipment and automation equipment; monitor the operation of electrical mechanisms; provide technical training; control the maintenance of an electrical journal; keep records of working hours;
(02) in difficult navigation conditions, be in the central control room or at the main switchboard (MSB) and manage the electromechanical watch. On ships with the sign of automation (A1, AZ) to be in the central control room or at the control panel on the bridge. If such a voyage lasts for a long time, he may, with the permission of the head of the service, temporarily leave the post, leaving behind the responsible specialist;
(03) before the departure of the ship for a voyage, not later than 2 hours before departure, report to the head of the service on the readiness of the department;
(04) when approaching the field, ensure that the electrical part of the production equipment is ready for operation;
(05) on call of the watchmen (assistant, mechanic, electromechanic, electrician) to immediately arrive at the place and stay there as long as the situation requires it;
(06) when assigned to a ship, accept from the supplier electrical equipment and automation equipment, spare parts, tools, inventory and documentation of his department. An act is drawn up on acceptance and delivery, and the transfer of cases is recorded in an electrical journal;
(07) when the ship is under repair, ensure electrical safety when supplying shore power; when docking or berthing, make sure that the ship's hull is grounded by the factory; control the parameters of the shore voltage and the ship's network.
113. On ships where there is a fourth electrician, the foreman does not keep watch, and where there is none, he keeps running watches from 08:00 to 12:00 and from 20:00 to 24:00. On ships where there is only one electrician, he performs the duties of the chief electrician.
114. The senior electrician, in agreement with the head of the service, draws up a schedule for departments and has the right to redistribute duties between his subordinates. On ships with an automation mark (A1, AZ), in the absence of an electrical watch in the engine room (CPU), he, in agreement with the ship's administration, sets the operating mode for electrical personnel.
Order of Roskomrybolovstvo of August 30, 1995 N 140 "On approval of the Charter of service on ships of the fishing fleet Russian Federation"> Appendix N 1. Charter of service on ships of the fishing fleet of the Russian Federation> Chapter VII. Ship mechanical service (clauses 72 - 132)
If you need an electrician, then2.1 The master is fully responsible for the training of trainees, authority can be delegated to the chief mechanic or electromechanic directly - who will have direct control over the daily training of trainees.
2.2 Practical classes for trainees-electromechanics are organized in the scope and in accordance with the training program for trainees established by the academic council of the department "ELECTRIC POWER" SMF, NSMA named after Admiral Ushakov F.F.
2.3 Interns should not be considered only as an additional workforce.
They should be involved in the working process of the ship, in order to implement part of
programs for their practical training and education. Recommended daily
involve the trainee in the work process and involve in assisting and duplicating
works on maintenance of the electric power plant of the ship.
2.4 The main direction of educational work on the flight is the preparation of trainees for mastering working qualification“ship electrician of the 2nd class” for cadets of the electromechanical specialty.
2.5 Under the guidance of experienced ship specialists, briefings, introductory
lectures, and tests are accepted on electrical safety, safety precautions, on deck and height work, on the organization of damage control and the use of life-saving equipment, on knowledge of emergency schedules.
2.6 At the end of floating practice, all cadets should have credits taken at their workplaces, and by order of the ship, admission to the independent performance of their professional duties in the specialty "electrician of the 2nd class" for cadets of the electromechanical specialty should be made.
INTERNSHIP TRAINING PROGRAM
This program provides for the study of the main types of work that are the duties of a class 2 ship electrician.
Classes are conducted by an electrician or St. ship mechanic who is the head of industrial training.
Before teaching each new operation or a new type of work, the leader is obliged to: explain to the trainee the purpose, content of the forthcoming work and technical requirements for it; give detailed instructions on safety and ship sanitation; to familiarize the trainee with the tools, fixtures, equipment and materials that are used in the work and the rules for using them;
In the process of performing production tasks by a cadet, the supervisor must systematically instruct him, promptly prompt and correct errors in work, cultivate a high work culture, skills for high-performance and high-quality performance of work, careful handling of equipment and tools, and economical use of materials and energy.
4 Marine Electrician Class 2 - Qualifications
As a result of passing the floating practice, a cadet applying for the assignment of the first professional level to him - a ship's electrician of the 2nd class must know and be able to:
1 prepare for operation, start, stop and service the units and mechanisms of the ship power plant, check the mode of their operation;
2 inspect, repair, adjust electrical equipment, detect faults and eliminate them;
3 supply power to the steering gear, winches, windlass (spire) and other electrically powered auxiliary machinery and systems of the ship;
4 carry out the simplest tests of electrical installations and accept the work performed;
5 to service the steering gear, winches, windlass (spire) and other electrified auxiliary mechanisms and systems of the ship;
6 prepare electrical equipment for conservation when the ship is placed in repair;
7 perform locksmith work on the processing of metals, plastics and on the manufacture of electrical equipment parts;
8 select tools, fixtures, materials for electrical work; use measuring tools and devices for measuring current strength, voltage, frequency, insulation resistance, etc .;
9 dismantle, repair, assemble and lay cables, power, lighting and signal equipment and devices on board the ship;
10 maintain and maintain command and service telephone communications in good condition;
11 to maintain and maintain in good order the station of signal and distinguishing lights,
searchlights and other light signaling devices;
12 repair, install lighting, starting, switching equipment and electric motors;
13 mount and connect group switchboards to the ship's network;
14 adjust and regulate the operating parameters of the electrical installation;
16 use life-saving equipment, know and be able to run the ADH, motorboat;
17 maintain forms and other established technical and reporting documentation on the ship's electrical equipment;
18 comply with safety regulations, industrial and ship sanitation, internal regulations, fire safety; rules for the technical operation of electrical equipment; duties on ship's schedules; provide first aid for injuries.
| Instructions for the position " Ship electrician 1st class", presented on the site, complies with the requirements of the document - "DIRECTORY qualification characteristics occupations of workers. ISSUE 67. Water transport. Section "Maritime transport" (With amendments and additions made by orders of the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Ukraine N 189 of 10.05.2005, N 671 of 06.08.2007). The second edition, supplemented, revised as of 08/06/2007 ", which was approved by order of the Ministry of Transport of Ukraine on 10.12.2001 N 863. Agreed by the Ministry of Labor and social policy Ukraine. The status of the document is "valid". |
|
Preface to job description
0.1. The document comes into force from the moment of its approval.
0.2. Document developer: _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
0.3. Document approved: _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
0.4. Periodic verification of this document is carried out at intervals not exceeding 3 years.
1. General Provisions
1.1. The position "Ship Electrician 1st class" belongs to the category "Workers".
1.2. Qualifications- complete general secondary education and vocational education. Advanced training and work experience on ships in the profession of a ship electrician of the 2nd class - at least 1 year.
1.3. Knows and applies:
- purpose, arrangement and principle of operation of the ship's electrical equipment;
- and ship electroautomatics;
- technology of electrical installation and repair work of the ship's electrical equipment;
- procedures for keeping a safe watch;
- power distribution systems on ships, methods of laying and repairing cable routes;
- purpose, arrangement and operation of ship automation, control, measurement and protection systems;
- device and principle of operation of ship battery installations and chargers, converters;
- the structure of ship automatic telephone exchanges and the rules for the maintenance of internal telephone communications;
- the basics of plumbing;
- basic protection actions environment;
- English language(marine specifics).
1.4. A ship's electrician of the 1st class is appointed to the position and dismissed from the position by order of the organization (enterprise / institution).
1.5. The ship's electrician 1st class reports directly to _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
1.6. The ship's electrician 1st class supervises the work of _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ .
1.7. The ship's electrician of the 1st class during the absence is replaced by a duly appointed person who acquires the appropriate rights and is responsible for the proper performance of the duties assigned to him.
2. Description of work, tasks and job responsibilities
2.1. Keeps watch according to the ship's schedule.
2.2. Provides Maintenance, repair and continuous operation of the ship's electrical equipment.
2.3. Eliminates malfunctions in the operation of ship electrical distribution devices, ballasts of ship electric drives, ship cable network, electrical fittings, etc.
2.4. Performs basic plumbing work.
2.5. Knows, understands and applies the current regulatory documents relating to its activities.
2.6. Knows and fulfills the requirements of regulatory acts on labor and environmental protection, complies with the norms, methods and techniques for the safe performance of work.
3. Rights
3.1. The Marine Electrician 1st Class has the authority to take action to prevent and remedy any irregularities or non-conformities.
3.2. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to receive all social guarantees provided for by law.
3.3. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to demand assistance in the performance of his official duties and exercise of rights.
3.4. A ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to demand the creation of organizational and technical conditions necessary for the performance of official duties and the provision necessary equipment and inventory.
3.5. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to get acquainted with the draft documents relating to his activities.
3.6. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to request and receive documents, materials and information necessary for the performance of his duties and orders of the management.
3.7. A ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to improve his professional qualifications.
3.8. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to report all violations and inconsistencies identified in the course of his activities and make proposals for their elimination.
3.9. The ship's electrician of the 1st class has the right to get acquainted with the documents defining the rights and obligations for the position held, the criteria for assessing the quality of the performance of official duties.
4. Responsibility
4.1. The ship's electrician of the 1st class is responsible for non-fulfillment or untimely fulfillment of the requirements of this job description obligations and (or) non-use of the granted rights.
4.2. The ship's electrician 1st class is responsible for non-compliance with the rules of internal work schedule, labor protection, safety measures, industrial sanitation and fire protection.
4.3. A 1st class ship's electrician is responsible for disclosing information about an organization (enterprise/institution) that is a trade secret.
4.4. The ship's electrician 1st class is responsible for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the requirements of internal normative documents organizations (enterprises/institutions) and legal orders of management.
4.5. The ship's electrician of the 1st class is responsible for offenses committed in the course of his activities, within the limits established by the current administrative, criminal and civil legislation.
4.6. The ship's electrician of the 1st class is responsible for causing material damage to the organization (enterprise / institution) within the limits established by the current administrative, criminal and civil legislation.
4.7. The ship's electrician of the 1st class is responsible for the misuse of the granted official powers, as well as their use for personal purposes.
Each vessel has the main regulatory and technical documentation for electrical equipment.
Assembly and circuit diagrams - giving an idea of the placement, the principle of operation of electrical installations. They are used in the repair or refurbishment and installation.
- Passports and forms, in which the technical data of electrical installations are entered, as well as data on their operation and changes in characteristics, failures, accidents and breakdowns, as well as repairs, tests, and records of regulatory authorities are made.
Technical instructions on the operation and description of the manufacturer's electrical equipment.
Vedomosti ZIP-list of spare parts for electrical equipment.
Electrical magazine, it contains basic data on the technical condition and operation of SES and other electrical equipment. Insulation resistance results, inspection, repair, faults, failures and breakdowns. The magazine is filled in by an electrician. Also, the ship must have documents: insulation resistance measurements, tables, acts, checklists of the SMS, TB, PRR, etc.
Fault detection of electrical equipment and automation equipment
Detection- designed to detect malfunctions, possible breakdowns and other undesirable consequences during the operation of electrical equipment. In accordance with the Register Rules, flaw detection is carried out special commissions and at certain times. With current repairs - 10 days, with an average of 15 days, with major repairs - one month. Fault detection is carried out with special tools and devices, as well as flaw detection of equipment.
Section 4
Operation and repair of EPS, electrical machines and systems on board
The operation of SEA includes organizational, technical measures aimed at maintaining the EPS in working condition, ensuring long-term and reliable operation, as well as electrical, fire and explosion safety.
The SEA, which ensures the management of the vessel and the safety of its navigation, must always be in good order and ready for operation.
It is forbidden: Operate the boat if the following units are out of order.
One DG out of two, or two out of three
Main light source and radio
Emergency power supplies
EP-steering gear
CSO, SIO.
Alarm and automation
Machine telegraph and other means of communication
It is forbidden: exploit electric cars if there are malfunctions that threaten the integrity of the electrical installation. Resistance 0.5 Mohm, sparking on the collector, failures of ballasts, current and temperature above normal, vibration, shaft beating, presence of electric shock.
Section 5
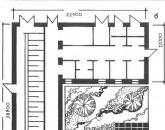
The composition of the ship SES:
· Plan-scheme of the engine room;
1, 2 -Station "ozone"
3- Cooling motor
4, 5- Outboard (sanitary) pumps
6,7,8 and 9-Pumps, fecal, waste, heat box and reserve.
10 - Fire pump
11 -system and heat box
12 -Battery box
13, 14 - Oil priming pumps
15 - Fuel pumps
16 -Separators
17 - Reserve fuel pump and service tank pump
18 - Oily water pumps
19 - Fuel transfer pump
20 -Compressor
Plan-scheme of placement of deck electrical equipment
1, 2- Windlass
3 -Towing winch
4 -Towing capstan
5 - Boat winches
6 - Cargo winches
Plan-scheme of the distribution of electricity on the ship
Section 6
Technical operation electric drives:
Windlass
With the help of anchor-mooring devices (spires, windlasses) on ships, the following operations are performed: anchor release (free pickling or electric drive), anchoring, mooring of the vessel.
YASHU electric drives must meet the following needs:
To be fed from the busbars of the main switchboard by separate feeders
Have sufficient power to raise the anchor, pull the ship up, lift at a speed of 0.12 m / s
Raise two free-hanging anchors at the same time
Operate at rated load for 30 minutes without interruption
Allow work and parking under current for 30 seconds.
To be reliable in the safe operation of the work
Simplicity and application in service.
boat winch
Boat winches installed on ships are designed for lifting and lowering crew members in emergency and working conditions. The work of the EP of the boat winch must ensure the safety of this operation, the special requirements of the regulatory authorities for it.
Self return to stop position
Control equipment should be located directly at the winch control station to ensure the safety of descent and control of all work operations.
When working in manual mode, the impossibility of turning on the electric drive.
Electrical equipment must be waterproof (IP44)
Steering gear
The steering gear is the most responsible of the ship's EP, since the maneuverability of the vessel and the safety of navigation depend on the operation of the steering device. Regulatory authorities impose special requirements on the EP of the steering device.
· ES of the Steering gear must provide:
Shifting the rudder from side to side at an angle of -35 0 +35 degrees at full speed in no more than 30 seconds.
Number of on / hour at least 350
Parking under current for 1 minute.
· The ES of Steering Gears shall provide for:
Starting device
Light signaling
Limit switches and protection against short-circuit currents.
The EP of the steering gear must have: reliability and ease of maintenance, small dimensions, quick transition from the main to the emergency control.
Steering EPs are divided: By type of PM: between the engine and the steering wheel, hydraulic transmission. According to the method of powering the engine, from the ship's network and through the main engine network. By the nature of the action - simple, tracking, and automatic action.
fire pump
Pumps are mechanisms designed to lift and move various liquids through the pipelines of ship systems. The pumps are divided into three groups: MKO pumps, marine systems pumps, and special pumps.
Fire pumps are classified as ship systems pumps. They are fed directly from the busbars of the main switchboard through separate feeders. Fire pumps have a power commensurate with the power of ship generators, so there is a limitation of starting current, it works in continuous mode. It has both local and remote switching on and off of the wheelhouse. The requirements are as follows:
Reliable performance and large water volume
Pressure 350/520 Kpas for cargo and oil tankers
Ease of maintenance
Protection against short circuit currents, overheating, minimum protection.
Popular
- Pigs for profit: we develop our business Profit from pig breeding at home
- Excursion to the Moscow brewing company Mytishchi Brewery
- Burger King: addresses, menu, delivery
- Russian refineries: main plants and enterprises The scale of Russian oil refining
- Business idea: release of board games
- Production of milk, dairy products
- Encyclopedia of Marketing. FMCG - what is it? The FMCG market and its marketing secrets What does fmcg mean
- Halva production and its types
- Working from home for retirees: ideas and analysis Maintaining a YouTube channel
- Earnings on YouTube for views Income on YouTube from 1000