Depreciation rate
A parameter expressed as a percentage of the price of fixed capital. Each year, services or goods are supplemented by this indicator.
Depreciation rate- the percentage of coverage of the price of the worn-out part of fixed assets on an annualized basis.
Depreciation rate: basic concepts, structure
The main purpose of introducing depreciation into the cost parameter of fixed assets is the economic coverage of moral and physical depreciation, which certainly takes place in the production process. As a consequence, depreciation can be represented as a smooth transfer of the price of fixed assets (the same equipment) to the goods they produce.
Depreciation deductions - a process that is carried out monthly by the relevant departments of the enterprise, taking into account the current book value of the OPF and depreciation rates. The basis is the breakdown of the above norms into various inventory items or groups of assets available on the company's balance sheet.
The rate of depreciation is the percentage established by the state to cover the price of fixed assets. Using the parameter, you can see the total amount of deductions during the year. In other words, - the ratio of two key parameters, namely the amount of depreciation (from the annual calculation) and the price of the enterprise's OPF. The parameter itself is expressed as a percentage.
The rate of depreciation is not fixed. It is established and reviewed by the relevant state structures. At the same time, the established norms are the same for all companies, regardless of the characteristics of the organization, the characteristics (field) of work and forms of ownership.
 The depreciation policy itself is the main element of the scientific and technological policy pursued at the country level. By putting down the rate and procedure for depreciation, the state is engaged in regulating the pace, as well as the nature of reproduction in a particular industry. In addition, it is easier to see the rate of depreciation through the depreciation rate, and with the help of the latter, the rate of restoration of the object.
The depreciation policy itself is the main element of the scientific and technological policy pursued at the country level. By putting down the rate and procedure for depreciation, the state is engaged in regulating the pace, as well as the nature of reproduction in a particular industry. In addition, it is easier to see the rate of depreciation through the depreciation rate, and with the help of the latter, the rate of restoration of the object.
The depreciation system was laid down in the era of the USSR. Their main features include a straight-line type of accrual, general depreciation rates and the accrual of two types of depreciation deductions (for the replacement of equipment and major repairs). This also includes the redistribution of depreciation between enterprises, the inclusion of depreciation in the price of a product (service), and so on.
Despite many similarities, since 1991 there have been certain changes in the depreciation rate. In particular, the following adjustments have been made:
1. New deduction rates have been established, which have significant differences for certain types of OPF.
2. Gone are deductions for overhaul. Now companies carry out all types of repair work at the expense of the cost of goods. At the same time, a separate one can be created, designed to carry out repair work.
3. Depreciation at the end of a certain period of service (norm) is terminated. In particular, this applies to vehicles, cars and other equipment. Previously, this work was carried out for the entire period of application. It did not matter for how long the technique was designed. As for the rest of the funds, the form and features of accrual for them remained unchanged (that is, accruals are made for the entire period of service).
4. There was a chance of accelerated depreciation for the active part of the production, for example, vehicles, equipment, machinery, and so on. There is a transfer of the balance price of these funds to the category of production costs. At the same time, the circulation period is reduced by almost two times. This is done in order to increase the level of interest of the company in the renewal of fixed assets.
In addition, small enterprises can write off fixed assets (up to 50% of the price) if the service life of such fixed assets is more than three years. With accelerated depreciation, there is a chance:
Quickly update the active share of production assets in the company (which is already quite a lot);
Transferred by the founders as an investment in the authorized capital of the company - at a price determined by the parties;
Purchased with money from other persons or companies at actual purchase and preparation costs;
Received free of charge from other persons or enterprises - at a price that has been determined by an expert.
Depreciation rates: methods and stages of calculation
In practice, the annual volume (rate) of depreciation deductions can be determined in one of the following ways:
1. Linear way. Here, the initial price of the OPF and the depreciation rate calculated taking into account the useful use of the object are taken into account.
2. Reducing balance method. The calculation is made taking into account the residual price of the OPF at the beginning of the year (the start of the reporting period), as well as the depreciation rate, taking into account the useful life of the funds.
3. Method of writing off the price by the number of years of use. The calculation is based on the original price of the BPF and the annual ratio of the number of years remaining until the end of service and the total period of application.
4. The method of writing off the price, taking into account (proportionately) the volume of work (goods). The peculiarity is the use of the natural parameter of the volume of work (goods) for and the ratio of the primary price of the object, as well as the implied volume of work (production) for the total period of useful use of the OPF.
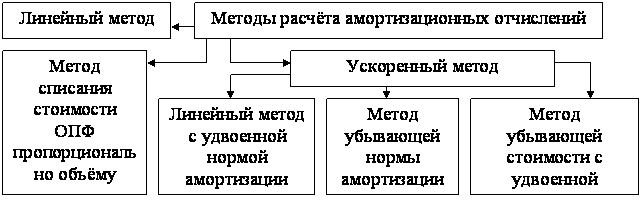
An important point is the planning of depreciation deductions. The more competently this process is planned, the better financial results can be achieved. The initial parameters for calculating depreciation allowances are:
OPF price parameters at the beginning of the period;
- prospective and annual payments for the introduction of the OPF. This also includes backgrounds coming from other companies;
- on projected disposal of fixed assets;
- Normalized parameters of depreciation charges.
The calculation of the total amount of deductions is made in several stages. For this you need:
1. Distribute fixed assets into groups that are provided for in the depreciation rates, and also calculate their value. It is important to take into account the need to deduct OPF, which includes equipment, vehicles, machines, depreciated funds, the service life of which has already expired.
2. Break down the average annual price of depreciable fixed assets into inventory items.
3. Calculate the volume of depreciation charges for a specific period of time for each of the inventory items or for a group of fixed assets by multiplying the average annual price by specific rates of depreciation charges. The calculation should take into account correction factors that reflect the actual operating conditions of these tools in the enterprise or in the workshop.
4. Calculate the total amount of depreciation charges for the future period (usually a year) for all depreciable funds by calculating the depreciation amounts (excluding depreciated funds related to transport, equipment, machinery).
The total amount of calculated depreciation should be charged to the cost of goods produced, services rendered or work performed. This process is carried out monthly. If we are talking about seasonal production, then the annual amount of depreciation should be included in the costs for the entire period of the company's operation in a year.
For fixed assets that have just been put into operation, depreciation is accounted for according to a special schedule. So, the starting point is the 1st day of the month, which immediately follows the month when the property began to be used. In turn, elimination occurs according to a similar principle. The only difference is that the month of elimination is taken as the starting point.
The total amount of depreciation charges is accumulated on the depreciation account and will be registered until the depreciable property is retired.
Proper application of depreciation charges, as well as taking into account their rate is very important for the company. First of all, the use of depreciation must be made for the successful implementation of enterprise policy.
Stay up to date with all important United Traders events - subscribe to our
Popular
- How to get a TIN: possible ways
- What kind of business can you do?
- Written notice of termination of the lease
- Business from scratch. Things to do?
- Cost of goods sold: formula, methodology and calculation example
- How to write a vacation application - examples
- What kind of business can be opened in a small town or village?
- The formula for calculating the cost of services, products sold and total cost
- Sample memorandum: I bring to your attention
- Example of an explanatory note for being late for work




