How to calculate the average annual cost of fixed assets?
The procedure for the OS accounting process is regulated by various legal acts.
The most significant documents here include:
- RAS 6/01 "Accounting for Fixed Assets" dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n;
- Guidelines for the accounting of fixed assets dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n.
These normative documents should also be based on the calculation of the average annual cost. The explanation for this is that, in addition to the purposes of accounting for fixed assets, conditions, the one-time observance of which is mandatory for the recognition of assets as such in the accounting process, etc., they regulate the procedure for forming their value.
In turn, the value formed in accordance with the rules set forth in these documents will subsequently be used to calculate the average annual value of these assets.
The calculation of the average annual value for the purpose of calculating property tax is based on a legal framework consisting of:
- P. 4, Art. 376 of the 2nd part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation of August 05, 2000 No. 117-FZ .;
- Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 15.07.2011. N 03-05-05-01/55.
Purpose of asset accounting
In accordance with clause 6 of the Guidelines, accounting for fixed assets pursues such goals as:
- accumulation of actual costs incurred associated with their acceptance into the accounting process;
- proper documentation and reflection in a timely manner of operations on their movement;
- determination of reliable results received from their sale and other disposals;
- calculation of actual costs incurred related to their content;
- ensuring proper control over the safety of assets accepted for the accounting process;
- analysis of the effectiveness of their use;
- getting OS information required for disclosure in the financial statements.
Asset value types
In accordance with the above legal acts, fixed assets have three types of value:
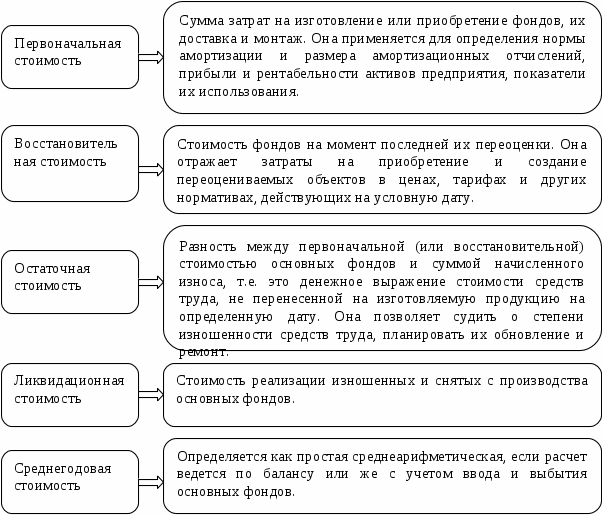
- Initial.
- Recovery.
- Residual.
The initial one is formed at the moment when the OS is being registered for accounting.
The procedure for its formation is set out in paragraphs. 8-11 PBU 6/01 and depends on how the organization obtains this type of assets:
- When buying or creating on your own, this is the amount of expenses actually incurred by the organization associated with the purchase or creation. It should be noted that paid VAT and other refundable taxes are not taken into account.
- When received as a contribution to the authorized capital of the organization is the value of the asset in monetary terms, agreed between the founders of the organization.
- When received as a gift is the market value of the asset as of the date of acceptance for accounting.
- Upon receipt under barter agreements is the value of the value transferred.
Changing the initial valuation is possible only in certain cases:
- with a major OS change. If they have been completed, retrofitted, reconstructed, modernized, partially liquidated;
- when re-evaluating the OS.
This list is exhaustive.
The replacement cost is formed:
- as a result of the restoration of property, involving a change in its original cost estimate;
- as a result of revaluation or markdown of property.
Residual value is the original (replacement) cost minus depreciation.
Methods for calculating the average annual cost
Without taking into account the month of input-output of fixed assets (formula)
If special accuracy is not required, then the average annual cost can be determined by the formula:
C-st (av) \u003d (C-st (n.g) + C-st (c.g)) / 2,
where С-st (n.g), С-st (c.g) - the cost of fixed assets, respectively, on January 1 and December 31 of the year for which the calculation is being made.
In this case, the cost as of December 31 is calculated by the formula:
C-st (k.g) \u003d C-st (n.g) + C-st (input) - C-st (select),
where C-st (input), C-st (select) - the cost of fixed assets, respectively, entered and written off during the year.
In all the above calculations, the book (residual) value of fixed assets should be used.
Taking into account the month of input-output of fixed assets (formula)
The most common formula used in calculating the indicators of the use of fixed assets (capital productivity, capital intensity, etc.):
S-st (avg) \u003d S-st (n.g) + M 1 / 12 × S-st (introduction) - M 2 / 12 × S-st (select),
where M 1 and M 2 are the number of full months that have passed, respectively, from the date of entry and write-off of fixed assets until the end of the year.
Chronological average formula:
C-st (avg) \u003d [(C-st (1n.m) + C-st (1k.m)) / 2 + (C-st (2n.m) + C-st (2k.m)) / 2 ... + (C-st (Nn.m) + C-st (Nk.m)) / 2] / 12,
where C-st (1n.m), C-st (2n.m), ... C-st (Nn.m) - the cost of fixed assets at the beginning of the 1st, 2nd, Nth month, respectively;
С-st (1k.m), С-st (2k.m), ... С-st (Nk.m) - the cost of fixed assets at the end of the 1st, 2nd, N-th month, respectively.
The formula used in calculating the average annual cost for calculating corporate property tax:
C-st (cp) \u003d (C-st (n1) + C-st (n2) + ... + C-st (nn) + C-st (c)) / 13,
where C-st (n1), C-st (n2) ... C-st (nn) - residual value of fixed assets on the 1st day, respectively, of the 1st, 2nd ... n-th month of the tax period;
C-st (k) - the residual value of fixed assets on the last day of the tax period (as of December 31 of the year for which the tax is considered);
13 - the number is obtained by adding one to 12 months of the tax period.
When calculating advance payments for 3, 6 and 9 months, the denominator of the calculation formula will be obtained by summing one with 3, 6 and 9 months, respectively.
The calculation of the residual value of fixed assets using this formula does not include the value of assets, the tax base for which is determined as their cadastral value.
Conclusion on the accuracy of methods
The calculation of the average annual cost using a formula that does not require taking into account the month when new fixed assets were introduced or old fixed assets were written off is the most inaccurate. To get a more accurate calculation, you must use one of those formulas that require such accounting.
In this case, the most reliable method of calculation is the calculation according to the chronological average formula. However, for calculating the average annual cost of fixed assets in order to determine the amount of property tax, a method other than that which has been described for this is unacceptable.
Noskova Elena
I have been in the accounting profession for 15 years. She worked as a chief accountant in a group of companies. I have experience in passing inspections, obtaining loans. Familiar with the areas of production, trade, services, construction.
Popular
- How to get a TIN: possible ways
- What kind of business can you do?
- Written notice of termination of the lease
- Business from scratch. Things to do?
- Cost of goods sold: formula, methodology and calculation example
- How to write a vacation application - examples
- What kind of business can be opened in a small town or village?
- The formula for calculating the cost of services, products sold and total cost
- Sample memorandum: I bring to your attention
- Example of an explanatory note for being late for work




